When President Biden first announced $1 billion in funding to install rooftop solar in Puerto Rico’s vulnerable communities two years ago, many Puerto Ricans felt it was cause for celebration. Federal officials have long sought to support rooftop solar in Puerto Rico, which could help the island's unstable energy grid become more energy-independent.
But under the leadership of President Trump — and with support from Puerto Rico’s newly elected governor, Jenniffer Gonzalez-Colòn — these federal dollars could end up going toward the island’s gas-heavy grid rather than renewable energy efforts.
On May 21, the Department of Energy announced it was redirecting $365 million from the Puerto Rico Energy Resilience Fund toward “technologies that improve system flexibility and response” for Puerto Rico’s power grid.
This fund was first established by the Biden Administration in February 2023, earmarking $1 billion in federal funding to build energy resilience for the island’s most vulnerable residents. Puerto Rico suffers from frequent blackouts and a notoriously unstable electric grid, and during natural disasters, rural communities are often without power for weeks or even months. The majority of the Energy Resilience Fund was intended to combat this by providing funding for rooftop solar installations on essential buildings, such as rural community health centers and the homes of low-income residents.
Since January, this funding has been slowly eroded. The first phase of funding, originally slated to provide $450 million for rooftop solar installations for low-income families, is set to be terminated in June, with less than half of its projects completed, according to grant recipients.
And with the May 21 announcement, experts are concerned that the final chunk of funding from this once-essential energy resilience fund will be redirected to Puerto Rico's existing energy infrastructure, much of which relies on coal and natural gas.
“These cuts are very dangerous because we don't really have a way to substitute those funds,” said Rolando Emmanuelli Jimenez, an attorney from San Juan and an expert on Puerto Rico’s energy sector. “Being a territory, we don't have the protection of equality among the states. So it's particularly worrisome that maybe the cuts in the states will be moderate, but here in Puerto Rico, they will be very profound.”
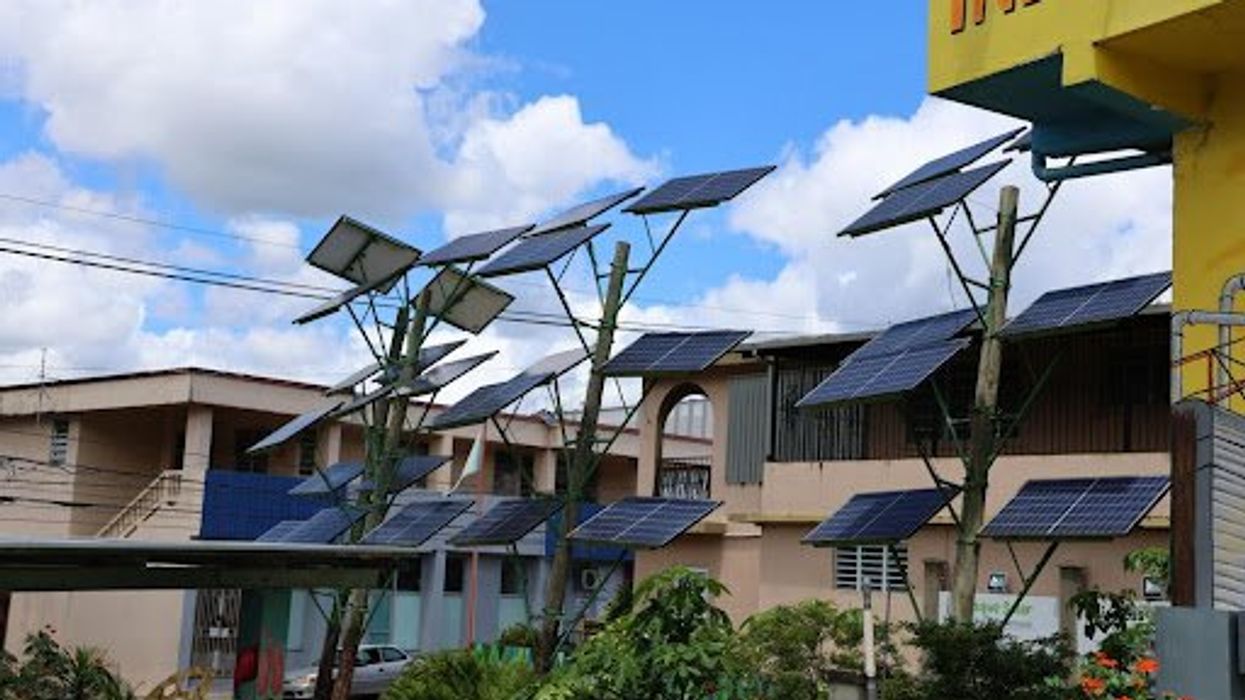
Solar is especially vital in Puerto Rico. The island’s maximum rooftop solar capacity is over 24 terawatt hours — that’s four times as much as its current residential energy consumption, according to a 2020 analysis by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory.
But currently, 93% of Puerto Rico’s grid runs on fossil fuels, and 85% of its energy resources are imported. The cost of energy per kilowatt-hour is higher than that of all but three U.S. states, primarily due to the high cost of importing fossil fuels. And under the management of two private corporations — LUMA Energy, which runs Puerto Rico’s transmission lines, and Genera PR, which runs its generation system — the government has lost much of its control over electricity prices.
Frustrated with the current electric system, many Puerto Ricans have turned to solar as a source of clean energy and a way to avoid the frequent blackouts under the LUMA-managed grid. The PR-ERF was just one of several funding streams designated by the Biden Administration for solar in Puerto Rico.
However, Governor Jennifer Gonzalez-Colón has faced backlash from some Puerto Ricans for her handling of energy policy since taking office in January, as well as for the changes to the Puerto Rico Energy Resilience Fund. While Gonzalez-Colòn had previously pledged to defend the island from Trump's funding cuts, her administration told the Associated Press in early May that she ultimately revoked her support for the Energy Resilience Fund. She has since publicly supported redirecting these grants to island-wide transmission systems.
“Rather than impacting a few customers, deploying these funds for urgent projects that improve the resiliency and reliability of our grid will have widespread, lasting benefits for all 3.2 million Americans in Puerto Rico,” Gonzalez-Colòn said in a May 21 press release announcing the change.
The first Trump administration had already authorized $18 billion in emergency funding to go toward system-wide transmission upgrades in Puerto Rico. These funds are currently frozen, but the new governor has recently pledged to ensure that federal authorities will deliver these funds.
In the wake of these policy changes, many Puerto Ricans — especially those in rural areas who have suffered from an unreliable electric system — were left feeling frustrated.
“The governor has made a political calculation to not go against the Trump administration, and is basically acquiescing to whatever the Department of Energy decides,” said C.P. Smith, executive director of Cooperativa Hidroeléctrica de la Montaña. “This is something that is very problematic.”
Since 2023, Cooperativa Hidroeléctrica has operated a solar microgrid in the mountain town of Castañer. This system links several solar panels into one small grid, enough to power a few dozen homes independently of the larger grid.
Cooperativa Hidroeléctrica received a grant from the Energy Resilience Fund as part of the Solar Ambassador Prize, which comprised the first $450 million of the fund. These grants were slated to go toward "last-mile communities" — rural households and towns, such as Castañer, that often experience the longest wait times for electricity restoration after blackouts.
“These are families that have suffered the most in terms of the poorest electric reliability,” said Smith.
Cooperativa Hidroeléctrica was planning to build 110 additional microgrids in rural neighborhoods over the next two and a half years. However, earlier this year, they discovered that their funding from the Energy Resilience Fund, as well as other grants from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, had been canceled.
According to Smith, there’s “no way” Cooperativa Hidroeléctrica can continue operating its existing microgrid, or move forward with building new ones, without federal funding.
“This is exactly the role of government with a capital G, right? Government steps in to take care of the cost of large infrastructure projects and other resiliency measures that cannot be attended to by the private sector, especially when we're talking about remote rural communities,” he said. “It doesn't mean that the government has to give giveaways, but those guaranteed loan programs are very important to be able to serve these communities that are poorly attended.”
Gonzalez-Colòn, a longtime Republican, has already followed some of Trump’s federal energy policy moves. The first law she passed was a package that eliminated Puerto Rico’s goals of transitioning to 40% renewable energy by 2025 and 60% by 2040. The law left the island’s ultimate goal of reaching 100% renewable energy by 2050 intact, but Gonzalez-Colòn hasn’t approved any new solar or wind projects while in office.
“Even the final renewable energy goal that was kept on the books, that is not going to be achieved,” said Ruth Santiago, an environmental lawyer based in Salinas, Puerto Rico. “All of these new gas power plants will take a few years to come online and have usually operational lives of 25 to 30 years.”
Gonzalez-Colòn also declared an "energy emergency," mirroring the one proclaimed by President Trump on his first day in office. The move drew attention to the island's power shortage and unstable grid, which could prove fatal as the Atlantic hurricane season approaches this summer. But according to Santiago, this could also be an attempt to speed up permitting for fossil fuel plants.
“Basically, the government is exempting all new energy, all energy infrastructure work, from Puerto Rico permitting requirements,” Santiago said. “They’re trying to sort of latch onto the federally declared energy emergency by President Trump, to potentially eliminate any permitting requirement, like Clean Air Act permits.”
Aside from the PR-ERF, federal funding cuts have also had indirect impacts on renewable energy research. Francisco Valentin, who runs a rural medical clinic in the mountainside province of Utuado, said his clinic has worked with U.S. universities for years. American students have visited Utuado to help provide healthcare to locals and to maintain the solar panels that power Valentin’s clinic.
In the wake of recent cuts to research universities, though, Valentin said he's nervous these programs might not continue. His clinic had already lost two grants from Fordham University, which would have amounted to $420,000. The University of Puerto Rico, which received over $51 million in total NIH grants across its campuses this year, has also begun to experience difficulties accessing databases for climate and renewable energy research.
“When you start to work with the communities, you can start to see that a lot of things that [need] help, and the people just have… the desire to be part of the solutions,” Valentin said. “But the government [isn't here]. They don't care. They don't have the resources.”
For now, both federal and Puerto Rican politicians say they're keeping fossil fuel plants running to ease the transition to renewable energy while also avoiding an energy shortage. Governor Gonzalez-Colòn plans to redirect some of the PR-ERF grant money toward building temporary fossil fuel plants and repairing aging ones.
“By redirecting these funds, we will ensure taxpayer dollars are used to strengthen access to affordable, reliable, and secure power, benefiting more citizens as quickly as possible,” said U.S. Energy Secretary Chris Wright in the May 21 press release.
However, given both Trump and Gonzalez-Colón's recent actions, experts like Emmanuelli are concerned that these temporary solutions could permanently put Puerto Rico on a path away from renewables.
“Right now, we don't know when we will have the capability in terms of renewable energy to substitute those new investments in natural gas,” Emmanuelli said. “I believe that the strategy for those sectors is to try to push hard here in Puerto Rico, to install temporary generation, to make them eventually permanent. So we will be tied to that energy that is not the best for Puerto Rico, that will make Puerto Rico a slave of the markets of natural gas.”
Lily Carey is a graduate student in journalism at Northwestern University.